Table of Contents
The following example creates a BLE server with a single service and characteristic. The characteristic can be read by a connected BLE client.
Steps:
- Set up the ESP32 as a BLE server.
- Advertise the server so that it can be discovered by BLE clients.
- Define a BLE service and a read-only characteristic.
- Allow the client to read the characteristic value.
Code:
#include <BLEDevice.h>
#include <BLEServer.h>
#include <BLEUtils.h>
#include <BLE2902.h>
// Define the BLE service and characteristic UUIDs
#define SERVICE_UUID "12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789abc"
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID "87654321-4321-4321-4321-abcdef123456"
// The characteristic value
const char* value = "Hello from Lonely Binary's ESP32!";
// Set up BLE server and characteristic
BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic;
BLEServer *pServer;
void setup() {
// Start Serial Monitor for debugging
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Starting BLE Server...");
// Initialize BLE device
BLEDevice::init("Lonely_Binary_ESP32_BLE_Server");
// Create BLE server
pServer = BLEDevice::createServer();
// Create a service
BLEService *pService = pServer->createService(SERVICE_UUID);
// Create a characteristic
pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
CHARACTERISTIC_UUID,
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ
);
// Set the initial value of the characteristic
pCharacteristic->setValue(value);
// Add a descriptor for the characteristic (optional)
pCharacteristic->addDescriptor(new BLE2902());
// Start the service
pService->start();
// Start advertising the BLE server
BLEAdvertising *pAdvertising = pServer->getAdvertising();
pAdvertising->start();
Serial.println("Waiting for client to connect...");
}
void loop() {
// Nothing to do in the loop, as BLE is handled in background
delay(1000);
}Explanation:
- BLEDevice::init(“Lonely_Binary_ESP32_BLE_Server”) initializes the BLE stack and gives the device a name (ESP32_BLE_Server).
- createServer() creates a BLE server.
- createService(SERVICE_UUID) creates a BLE service using a unique UUID (12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789abc).
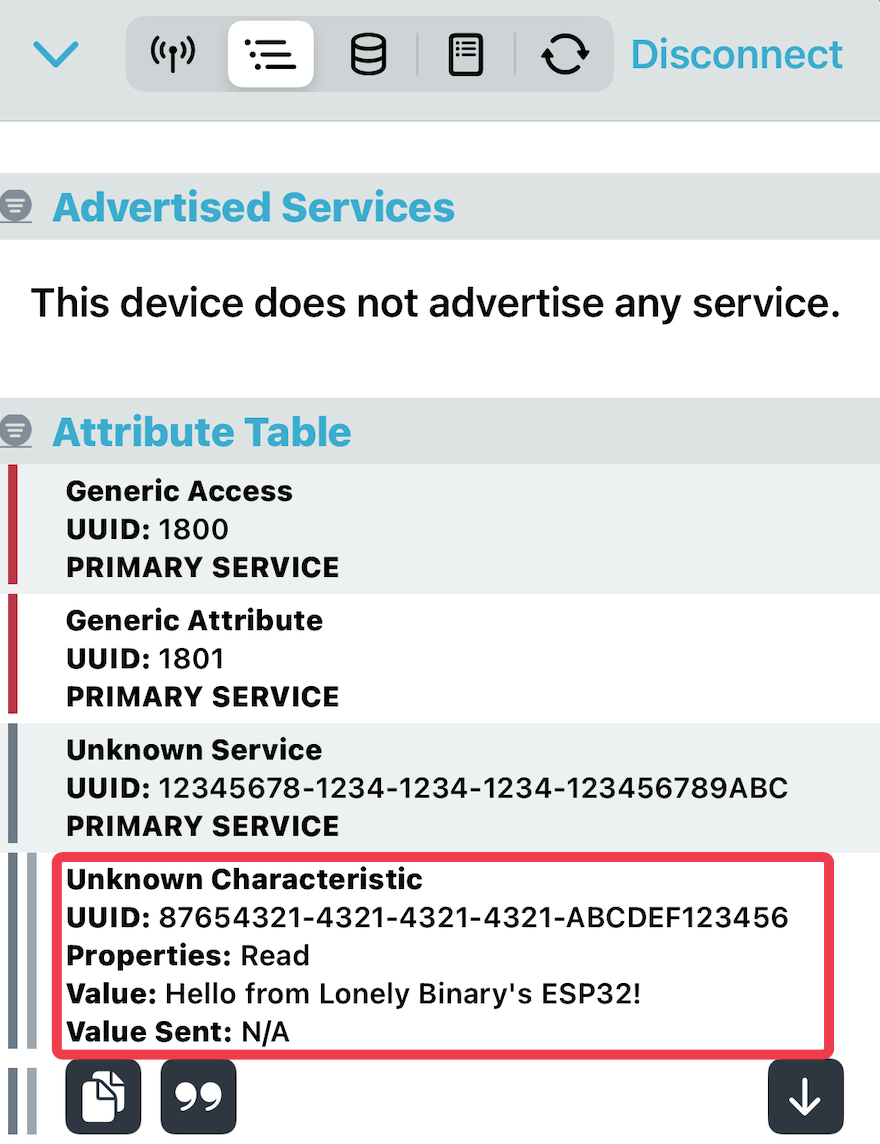
- createCharacteristic(CHARACTERISTIC_UUID, BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ) creates a read-only characteristic with a unique UUID (87654321-4321-4321-4321-abcdef123456).
- setValue(value) sets the initial value of the characteristic to “Hello from Lonely Binary’s ESP32!.
- getAdvertising()->start() starts advertising the BLE server, so it can be discovered by BLE clients.
How to Test:
- Upload the code to your ESP32.
- Use a BLE client app nRF Connect for mobile on your phone.
- Search for ESP32_BLE_Server in the BLE client app and connect to it.
- Once connected, you should be able to read the characteristic value (“Hello from Lonely Binary’s ESP32!”).